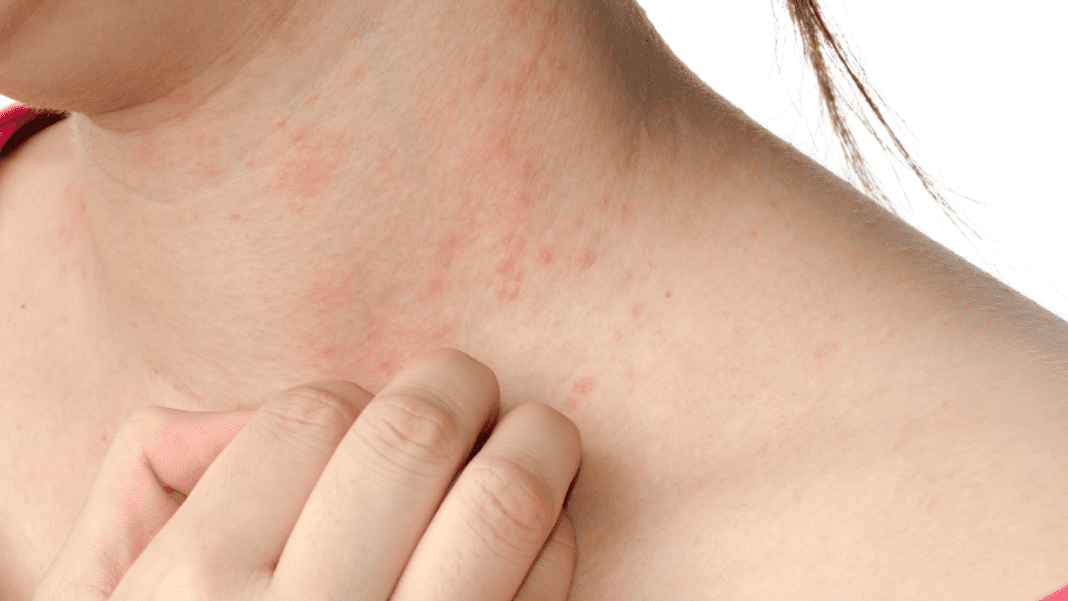
Are Hives Contagious? Understanding the Causes and Transmission of Hives
Hives, also known as urticaria, are a common skin condition characterized by raised, red, itchy welts on the skin. Many people wonder whether hives are contagious and how they can be transmitted. The answer is that hives themselves are not contagious, but the underlying causes may be. Hives can be caused by a variety of factors, including allergies, infections, stress, and certain medications. If an infection or allergic reaction is the cause, it may be contagious.
However, hives themselves cannot be transmitted from person to person through contact. It’s important to understand the underlying cause of hives to prevent their recurrence and properly treat the condition. In this article, we will explore the causes of hives, how they are transmitted, and whether or not they are contagious.
What Causes Hives?
Hives are typically caused by an allergic reaction, although they can also be caused by other factors such as stress, infection, or certain medications. When the body comes into contact with an allergen, such as pollen or pet dander, it releases a chemical called histamine. Histamine causes the blood vessels to dilate, leading to swelling and inflammation in the skin, resulting in hives.
Other potential causes of hives include:
- Infections, such as viral or bacterial infections
- Stress or emotional upset
- Exposure to extreme temperatures
- Sun exposure
- Certain medications, such as antibiotics or pain relievers
- Foods, such as nuts, shellfish, or eggs
- Insect bites or stings
How are Hives Transmitted?
Hives are not contagious, which means they cannot be transmitted from one person to another through direct contact or airborne particles. This is because hives are not caused by a virus or bacteria, but rather by an allergic reaction or other underlying condition.
However, if someone is exposed to the same allergen that caused another person’s hives, they may also develop hives as a result of their allergic reaction. For example, if two people are allergic to the same type of pollen and are both exposed to it, they may both develop hives.
Similarly, if someone comes into contact with an object that has been contaminated with an allergen, such as a piece of clothing that has pet dander on it, they may develop hives as a result of their exposure.
Are Hives Contagious?
In short, no, hives are not contagious. As we discussed earlier, hives are not caused by a virus or bacteria, but rather by an allergic reaction or other underlying condition. Therefore, you cannot catch hives from someone else, and you cannot give them to someone else.
However, if you have hives, it is important to avoid contact with others if possible, particularly if your hives are severe or if you are experiencing other symptoms such as fever or difficulty breathing. This is because severe hives can sometimes be a symptom of a more serious allergic reaction, which can be life-threatening in some cases.
How Are Hives Caused?
Hives or urticaria are usually triggered by an allergic response resulting in the release of histamine in the skin.
These triggers can be foods, medicines, chemicals, or even certain medical conditions and can result in the development of hives over the entire body or a part of it such as the arms, legs, or stomach.
Hives may develop within a few minutes of contact with the triggering agent or it may take hours after exposure to the triggering agent for the hives to develop and they usually disappear within 24-48 hours after the exposure ends. In a few rare cases, hives may persist for days or weeks in which case it is termed chronic urticaria.
What Are The Common Triggers For Hives?
Triggers are difficult to identify as even overexposure to heat or cold can result in hives but common triggers are usually:
- Foods such as certain fruits like strawberries and kiwis or seafood such as shrimp and oysters.
- Drugs such as penicillin and sulfa.
- Infections are caused by bacteria, viruses, or even parasites.
- Certain Insect bites
- Exposure to Pollen
How to Prevent Hives?
The best way to prevent hives is to identify and avoid the allergen or trigger that is causing them. This may require some trial and error, as it can be difficult to identify the specific allergen that is causing your hives.
If you do develop hives, there are several things you can do to relieve the symptoms, including:
- Taking antihistamines
- Applying cool compresses to the affected area
- Avoiding hot showers or baths
- Using fragrance-free soaps and detergents
- Wearing loose, breathable clothing
In some cases, your doctor may prescribe corticosteroids or other medications to help relieve the symptoms of hives.
4 Effective Home Remedies for Hives
Hives, or urticaria, can be uncomfortable and itchy. Here are four effective home remedies for hives:
- Oatmeal Bath: Oatmeal has natural anti-inflammatory properties that can soothe irritated skin. To make an oatmeal bath, mix 1 cup of uncooked oats in warm water and soak in it for 20-30 minutes.
- Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress to the affected area can reduce inflammation and relieve itching. Wrap ice cubes in a cloth or use a cold pack and apply it to the hives for 10-15 minutes at a time.
- Aloe Vera Gel: Aloe vera gel has anti-inflammatory and soothing properties. Apply fresh aloe vera gel to the affected area to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Apple cider vinegar has antihistamine properties that can help reduce inflammation and itching. Mix equal parts apple cider vinegar and water and apply it to the hives with a cotton ball.
These remedies can provide temporary relief from hives, but it’s important to identify and treat the underlying cause of hives to prevent their recurrence. If the hives persist for more than a few days or are accompanied by other symptoms such as difficulty breathing or swelling of the face, seek medical attention immediately.
Over-the-counter Medications for Hives
Now in the market, there are certain chemical creams and ointments containing antihistamines that effectively counteract your body’s histamine response and give you fast relief from the itchiness and irritation you suffer on your skin due to hives. Take a look at some phenomenal antihistamine-based products.
-
Calamine Lotion
Calamine lotion is used for ages to give you cooling relief from all skin rashes including hives. They are very flexible to use, you just need to shake the bottle before use so that all its ingredients are thoroughly mixed and then squeeze a coin size of the lotion on a cotton ball and dap it on the affected skin areas. You will get quick relief against the troublesome itchiness of the hives and also feel a cooling sensation on your skin.
-
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
Now, this is an oral antihistamine medicine that can be very beneficial to relieve the symptoms of a hive. You would get desired results just within an hour of consuming this medicine. Although this medicine is very effective, be careful in taking appropriate dosages as specified in the pack. Also due to this medicine, you may encounter some dizziness, Don’t worry you would feel normal again in some time. If not immediately visit the doctor.
-
Fexofenadine (Allegra), loratadine (Claritin), and cetirizine (Zyrtec)
These antihistamine pills have better efficiency as compared to conventional diphenhydramine as the intake of these medicines doesn’t make you feel drowsy as the intake of these medicines. And they are in time-oriented 12-hour and 24-hour formulas, based on which you stay relieved from the symptoms of hives for that period as well as even if the effect of these medicines fade still there are residual benefits of it on your body.
Prescription Options For Hive Bites
If symptoms of hives get severe, the above home remedies, natural treatment, and basic medicines cannot control your deteriorating health due ill effects of hives. In such cases, only doctors and their prescribed medicines can come to your rescue.
Below are some of the most common and effective medicines prescribed by the doctor to treat hives issues.
-
Prednisone (Deltasone)
This is a type of corticosteroid pill and should be taken only on the doctor’s advice that the doctor prescribes it only for some days until the severity of hive symptoms reside. Extended use of these medicines without a doctor’s advice can lead to some severe side effects on your body such as
- Increase in weight
- High blood pressure
- Cataract problems
- Weakening of the natural immune system of the body
- Hormonal imbalance in the body
You can also opt for corticosteroid topical creams by taking a doctor’s advice as they know better to prescribe the right medicine depending upon the severity of the symptoms your body is subjected to.
-
Leukotriene-receptor antagonists
These are the non-steroid type of pills that are recommended by the doctor when the steroids and antihistamine medicines are not able to bring the symptoms of hives under control.
There are potential side effects if you consume overdose on this medicine such as mild fever, headache, diarrhea, and cough.
-
Omalizumab (Xolair)Dapsone (Aczone)
Now, these medicines need to be injected through a syringe into your skin. The doctor prescribes this medicine only if you are suffering from prolonged hive symptoms for a month or more. This medicine also has potential side effects such as flu-like symptoms, headache, ear pain, and dizzy feeling.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hives themselves are not contagious. They are common skin conditions that can be caused by a variety of factors, including allergies, infections, stress, and certain medications. If an infection or allergic reaction is the cause of hives, it may be contagious. However, hives themselves cannot be transmitted from person to person through contact. It’s important to understand the underlying cause of hives to prevent their recurrence and properly treat the condition. While home remedies can provide temporary relief from hives, it’s always a good idea to consult with a medical professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
FAQs on Hives Contagiousness
Q1. Are hives contagious from person to person?
Ans. No, hives themselves are not contagious and cannot be transmitted from person to person through contact.
Q2. Can hives be caused by a contagious illness?
Ans. Yes, hives can be caused by an infection or allergic reaction that is contagious. For example, hives may be a symptom of a viral infection such as the common cold or the flu.
Q3. Can hives be spread by sharing personal items?
Ans. No, hives cannot be spread by sharing personal items such as clothing, towels, or bedding.
Q4. Can hives be contagious through saliva?
Ans. No, hives cannot be spread through saliva or other bodily fluids.
Q5. How can I prevent the spread of hives if they are caused by a contagious illness?
Ans. If hives are caused by a contagious illness, it’s important to practice good hygiene such as washing your hands frequently, covering your mouth when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with others until you are no longer contagious. Additionally, seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment to prevent the recurrence of hives.