Welcome, dear reader, to the comparison of Chiggers vs. Scabies! These two skin-irritating foes are notorious for causing discomfort and confusion, often leaving their victims scratching their heads (and their skin) in bewilderment. It’s time to unravel the mystery and put an end to the itching once and for all.
In this riveting article, we’ll delve into the worlds of chiggers and scabies, shining a light on their unique characteristics, symptoms, and treatments. As we navigate the nitty-gritty of these minuscule marauders, you’ll learn how to differentiate between their bites, saving you time and anguish in your quest for relief. So, strap in and prepare for an epic showdown as we pit chiggers against scabies in a head-to-head battle for your skin’s well-being. Who will emerge victorious? Let’s find out!
What Are Scabies and Chiggers?
Scabies is a skin condition caused by infestation with the mite Sarcoptes scabies. The mites burrow into the top layer of skin and lay their eggs, causing itching and redness. Scabies are highly contagious and can be transmitted through close physical contact with an infected person, or through sharing clothes or bedding. It is more common in crowded, unsanitary living conditions, but can also be transmitted in hospitals, nursing homes, and other healthcare settings.
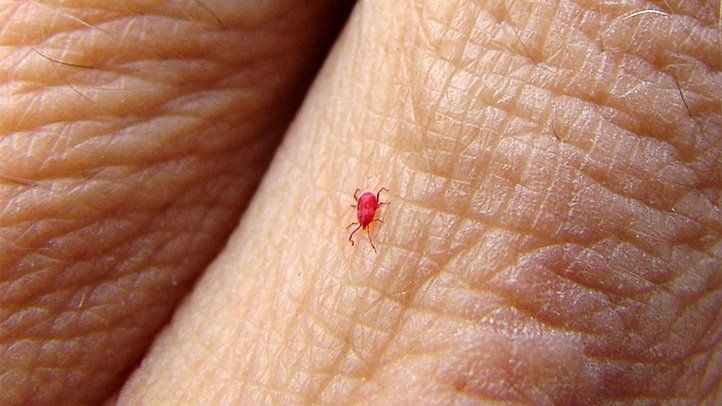
Chiggers are tiny, red mites that belong to the family Trombiculidae. They are found in grassy and wooded areas, particularly in areas with high humidity. Chiggers do not burrow into the skin, but instead, attach themselves to the skin and inject a small amount of saliva that dissolves skin cells, allowing them to feed on the resulting liquid. This can cause red, itchy welts on the skin. Chiggers are most often transmitted through direct contact with infested grass or vegetation, but can also be transmitted through contact with infected animals.
Chiggers vs Scabies- Transmission
Scabies and chiggers are both types of parasites that can be transmitted from one person to another.
Scabies is a skin condition caused by infestation with the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. The mites burrow into the top layer of skin and lay their eggs, causing itching and redness. Scabies are highly contagious and can be transmitted through close physical contact with an infected person, or through sharing clothes or bedding. It is more common in crowded, unsanitary living conditions, but can also be transmitted in hospitals, nursing homes, and other healthcare settings.
Chiggers are tiny, red mites that belong to the family Trombiculidae. They are found in grassy and wooded areas and feed on the skin cells of animals and humans. Chiggers do not burrow into the skin, but instead inject a small amount of saliva that dissolves skin cells, allowing them to feed on the resulting liquid. This can cause red, itchy welts on the skin. Chiggers are most often transmitted through direct contact with infested grass or vegetation, but can also be transmitted through contact with infected animals.
Both scabies and chiggers can be treated with medications prescribed by a healthcare provider. It is essential to follow the treatment instructions carefully to ensure that the parasites are eliminated and prevent reinfection. In addition, it is essential to practice good hygiene and avoid close physical contact with infected individuals to prevent the transmission of scabies and chiggers.
Chiggers vs Scabies- Symptoms
Chiggers and scabies have different symptoms. Chigger bites cause intense itching and a red bump on the skin. The bites usually appear in groups around the waist, ankles, or behind the knees. In contrast, scabies infestations cause a rash and severe itching, especially at night. The rash often appears on the wrists, between fingers, and around the waist. It’s important to note that chigger bites and scabies infestations can be mistaken for other skin conditions, so it’s important to seek medical attention if you’re unsure of the cause of your symptoms. Below I have mentioned various symptoms of scabies and chiggers to help you differentiate between each other.
Symptoms of Scabies
Scabies is a skin condition caused by an infestation of the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. It is characterized by intense itching and a rash. The most common symptoms of scabies include:
- Itching that is often severe and worse at night
- A rash that appears as raised red bumps or blisters
- Thin lines or burrows on the skin, especially in folds of the skin such as between the fingers, under the arms, or on the buttocks
- Scaly or flaky skin
- Small red bumps or nodules on the skin, especially on the wrists, elbows, or penis
- Swelling and redness around the bumps or nodules
If you think you may have scabies, it is important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of Chigger Bites
Chiggers are small, red mites that are found in grassy or wooded areas. They can bite humans and cause skin irritation, which is often referred to as “chigger bites” or “redbug bites.” The most common symptoms of chigger bites include:
- Itching that is often intense and may persist for several days or weeks
- Small, red bumps or welts on the skin, often in clusters
- Swelling and redness around the bites
- Pain or tenderness in the affected area
Chigger bites can be very uncomfortable, but they are generally not serious and will resolve on their own over time. To help relieve the itching and discomfort associated with chigger bites, you can try using over-the-counter creams or ointments, taking an antihistamine, or applying a cold compress to the affected area. If you have a severe reaction to chigger bites or if the bites become infected, you should see a doctor.
- Check Chigger Relief Creams
- Chigger Relief Liquids
- Chigger Relief Sprays
- Top Rated Chigger Relief Products on Amazon
Chiggers vs Scabies- Treatment Options
For Chiggers, treatment usually involves washing the affected area with soap and water, followed by the application of topical anti-itch cream or lotion. Over-the-counter antihistamines may also provide relief. For Scabies, prescription creams containing permethrin or ivermectin are typically used to kill the mites and their eggs. It is important to treat all family members and close contacts. In severe cases, oral antibiotics or corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and control itching. Consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How To Treat Scabies?
Scabies is a skin condition caused by an infestation with the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. It is characterized by intense itching and a rash. Treatment options for scabies include the following:
- Medications: The most common treatment for scabies is prescription medications that kill the mites. These medications include permethrin cream and crotamiton cream. They are applied to the entire body from the neck down, left on for a specified amount of time, and then washed off.
- Topical ivermectin: This medication is an oral medication that is taken by mouth. It is effective in treating scabies but is not yet approved for this use in the United States.
- Lindane: This medication is a prescription lotion that is applied to the entire body from the neck down. It is not as commonly used as other treatments due to potential toxic side effects.
- Sulfur ointment: This is an over-the-counter treatment that can be effective in treating scabies. It is applied to the affected areas and left on for a specified amount of time before being washed off.
It is important to follow the instructions for the medication you are using and to complete the entire course of treatment to ensure that the mites are fully eradicated. In addition, it is important to wash bedding, clothing, and towels in hot water to remove any mites that may be present.
How To Treat Chigger Bites?
Chiggers, also known as red bugs, are tiny mites that can cause intense itching and inflammation. If you have been bitten by chiggers, here are some treatment options:
- Wash the affected area with soap and water: This can help to remove any remaining chiggers and reduce the risk of infection.
- Apply an over-the-counter cream or lotion: Products containing hydrocortisone or calamine lotion can help to reduce itching and inflammation.
- Take an antihistamine: Antihistamines can help to reduce itching and swelling.
- Apply a cold compress: Placing a cold compress on the affected area can help reduce itching and swelling.
- Avoid scratching: It can be tempting to scratch chigger bites, but this can cause the skin to break and increase the risk of infection. Try to resist the urge to scratch and use other methods to reduce itching instead.
- Seek medical attention if necessary: In rare cases, chigger bites can cause a severe allergic reaction or infection. If you experience difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or if the bites become infected, seek medical attention immediately.
It is important to keep the affected area clean and to avoid scratching to reduce the risk of infection and further irritation. If you are experiencing severe or persistent symptoms, or if you have a weakened immune system, you should speak to a healthcare professional for further guidance.
Some homemade remedies can help if the infection is not severe. You can apply neem paste, aloe vera gel, and tea tree oil to get some relief.
Chiggers vs Scabies- Preventive Measures
Preventing chiggers and scabies infestations involves taking some simple precautions. When spending time outdoors, wear long sleeves and pants to minimize skin exposure. Apply insect repellent containing DEET to exposed skin, and treat clothing with permethrin. Avoid walking through tall grass or sitting on the ground, where chiggers may be present. To prevent scabies, avoid skin-to-skin contact with infected individuals, and don’t share clothing or bedding with them. Wash your hands frequently, and keep your home clean and sanitized. By following these prevention measures, you can reduce your risk of chigger and scabies infestations in the United States. For your convenience, I have mentioned the preventive measures for scabies and chiggers in detail below.
What Are the Preventive Measures for Scabies?
Here are some steps you can take to prevent scabies:
- Wash your hands frequently: Scabies is spread through direct skin-to-skin contact, so washing your hands frequently can help reduce the risk of transmission.
- Avoid close contact with infected individuals: If you know someone who has scabies, try to avoid close physical contact until they have received treatment and the mites have been eliminated.
- Wash bedding and clothing regularly: Mites can survive for a short period on bedding, clothing, and towels. Wash these items in hot water to kill any mites that may be present.
- Avoid sharing personal items: Scabies can be transmitted through the sharing of personal items such as combs, brushes, hats, and towels. It is best to avoid sharing these items, particularly if you are in a high-risk environment such as a nursing home or correctional facility.
- Use protective barriers: If you are in a high-risk environment, you may want to consider using protective barriers such as gloves and gowns to reduce the risk of transmission.
- Practice safe sex: Scabies can be transmitted through sexual contact, so it is important to practice safe sex and use condoms to reduce the risk of transmission.
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of contracting scabies and help prevent their spread to others.
What Are the Preventive Measures for Chigger Bites?
Here are some steps you can take to prevent chigger bites:
- Wear protective clothing: Chiggers are often found in tall grass and vegetation, so wearing long sleeves and pants can help to prevent them from coming into contact with your skin.
- Use insect repellent: Products containing DEET can help to deter chiggers and other insects.
- Avoid areas with high populations of chiggers: Chiggers are more commonly found in certain areas, so try to avoid spending time in areas where they are known to be present.
- Check for chiggers before coming inside: If you have been in an area where chiggers are present, check your clothing and skin for any chiggers before coming inside. Remove any that you find and wash your clothes to prevent them from spreading.
- Keep grass and vegetation trimmed: Chiggers prefer to live in tall grass and vegetation, so keeping these areas trimmed can help reduce the population of chiggers in your yard.
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of being bitten by chiggers and the discomfort that comes with it.
Concluding Chiggers v/s Scabies
Overall, scabies and chiggers are uncomfortable but not serious health problems that can be treated with proper medical attention. It is essential to take preventive measures to avoid getting these parasites and to seek treatment if you suspect you may have been infected.
People also search for –
- What do Chiggers look like?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Chiggers
- Can Chiggers Live in My Bed?
- How to get rid of Chiggers?